What is function of circuit breaker? Types of Circuit Beaker?
What is function of circuit breaker? Electrical systems rely heavily on circuit breakers for safety and overload prevention. These protective switches automatically cut off electricity when they detect faults or unusual currents. By swiftly interrupting electrical flow, circuit breakers are crucial in averting potential fires and electrical damage, thus ensuring safety in residential and commercial structures. This post will explore the diverse functions and related significant topics of What is function of circuit breaker in electricity method. Others Topic
Understanding the Basics of Circuit Breakers
To grasp the specific functions of circuit breakers, we should first understand their basic operation. A Circuit breakers consist are two mechanisms. They are- 1. switch mechanism & 2. tripping mechanism. The switch controls the circuit’s open or closed state, while the tripping mechanism monitors current abnormalities and activates the switch when necessary.
During normal operation, the circuit breaker’s switch keeps the circuit closed, allowing unimpeded electricity flow. However, if an issue like a short circuit or overload occurs, the tripping mechanism activates. This rapid response prevents potential hazards such as overheating or fires that could result from excessive current.
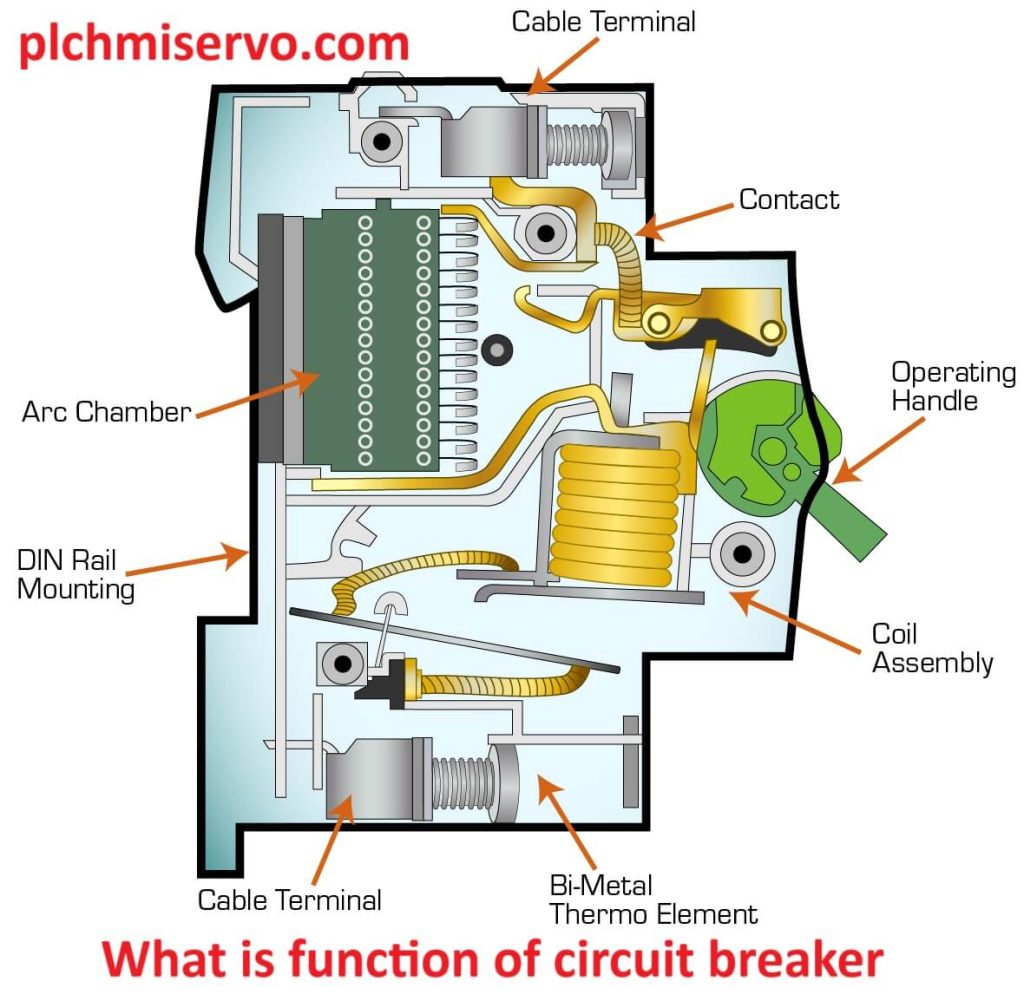
Components of a circuit breaker
Here some components of circuit breaker are given below:
1. Control Device: A manual switch or lever that allows users to open or close the circuit as needed.
2. Fault Detection System: An electromagnetic or thermal component unit that monitors the current flow.
3. Conductive Pathways: A set of movable conductive plates that either connect to allow current flow (closed position) or separate to stop it (open position).
4. Arc Suppression Unit: A component designed to quickly extinguish the electric arc that forms between the Conductive Pathways when the circuit opens, protecting the device and ensuring safe current interruption.
5. Actuation Mechanism: The system responsible for physically moving the conductive pathways to open or close the circuit, often using springs or a motor.
Main Working Principle of Circuit Breaker
Here’s the Working Principle and breakdown of their operation:
1. Detecting Trouble: Circuit breakers are equipped to sense electrical issues like overcurrent (too much current) or short circuits. This detection is often built-in, especially for household breakers.
2. Tripping Mechanisms: Two main mechanisms trigger a circuit breaker trip:
+Electromagnetic Trip: Responds to the magnetic field of excess current during an overload.
+Thermal Trip: Uses a bimetallic strip that bends due to heat from overcurrent, initiating a trip.
3. Contact Separation: Next, the breaker opens its contacts, creating a gap in the circuit. This mechanism halts electricity, safeguarding the circuit and its connected devices from additional harm.
4. Current Interruption: Separating the contacts cuts the power. This swift interruption is critical for protecting the circuit and equipment from potential harm.
5. Arc Suppression: The opening process can generate an electric arc. Circuit breakers use various methods like arc chutes or extinguishing media (e.g., oil or gas) to safely quench this arc and ensure complete circuit interruption.
6. Resetting Power: Some breakers allow for manual reset.
The functions of circuit breaker
Key circuit breaker functions:
+Overcurrent protection
This main working principle of circuit breaker. Without this vital safety measure, electrical systems could be damaged by excessive current. Overcurrent can result from various issues such as short circuits, faulty equipment, or power surges. Circuit breakers are responsible for monitoring, protecting and safeguarding the current within a circuit. When they detect an excessive current flow beyond a set threshold, they automatically “trip” or switch off.
This action disconnects the circuit from its power source, halting the current flow and preventing further damage to the wiring, connected devices, and overall electrical system. By instantly reacting to overcurrent situations, circuit breakers play an indispensable role in sustaining electrical security and averting potential hazards. Their ability to quickly detect and react to dangerous current levels helps protect both the power source and the entire circuit, including all connected equipment.
+Short Circuit Protection
Unplanned connections between conductors with substantial voltage differences result in short circuits. These events cause a rapid increase in current, potentially harming circuits and connected equipment, and may even lead to fires or explosions. These protective devices are designed to identify and counteract short circuit faults.
Upon detecting a weak-resistance line caused by a short circuit, circuit breakers swiftly cut off power to the affected circuit. This rapid intervention helps prevent overheating. It also lowers the fire chance from various electrified sources.
+Device Protection
Acting like a safety switch, circuit breakers guard electrical appliances, equipment, and wiring from harm caused by too much electricity. When problems arise with the current flow, they cut the power, preventing damage and keeping everything functioning properly in the long run.
+Selective Coordination
For intricate electrical systems, circuit breakers can be strategically planned to act like guards for specific zones. This way, if a problem occurs in one area, only that section loses power. The remaining components are performing optimally. This clever coordination ensures a more dependable and uninterrupted flow of electricity, especially for crucial applications.
+Manual Control
Circuit breakers come with a handy manual switch. This lets you turn the power on and off yourself, which is helpful when fixing electrical problems or performing maintenance.
+Arc Fault Protection
Regular circuit breakers are great, but some advanced ones go a step further. They can act like extra fire alarms, sensing dangerous electrical sparks (arcing) and shutting off the power to prevent fires. This adds an extra layer of safety in homes and businesses.
+Ground Fault Protection
Circuit breakers contribute significantly and effectively in ground fault protection. Ground faults happen when an energized conductor makes contact with a grounded surface or component in the electrical system. This can result from deteriorating insulation, accidental contact, or human mistakes. When a ground fault occurs, the circuit breaker identifies an uneven current flow between the live and neutral conductors. It then swiftly cuts off the circuit, isolating the problematic area from the power supply.
This action prevents potentially fatal electric shocks and mitigates electrical dangers. In certain areas like bathrooms or kitchens, specialized circuit breakers known as Ground Fault Circuit Interrupters (GFCIs) are used. These devices offer enhanced protection by detecting irregularities in electrical current flowing to the ground, thus providing an extra safeguard against electric shock hazards.
+Fire Protection
Circuit breakers are crucial in preventing electrical fires. These fires can start from overloads, short circuits, or faulty wiring. When electrical current surpasses the capacity of wires or components, it generates excessive heat that can ignite nearby combustible materials. The fire prevention role of circuit breakers stems from their ability to detect and respond to overcurrent’s and short circuits.
Upon detecting such concerns, the circuit breaker immediately turn off the electricity performing like a switch. This rapid action eliminates the heat source that could potentially start a fire. By offering this dependable and effective fire prevention function, circuit breakers significantly enhance the safety of electrical systems.
+Switching and Isolation
Beyond protection, they’re also essential for switching and isolation. When maintenance or repairs are needed, these devices allow for safe power disconnection, shielding workers from live electrical contacts and reducing accident risks. Additionally, circuit breakers segregate individual circuits. This isolation prevents fault propagation, confining issues to their origin points. As a result, they help maintain the overall system’s stability and dependability. For details you can see the What is function of circuit breaker?
